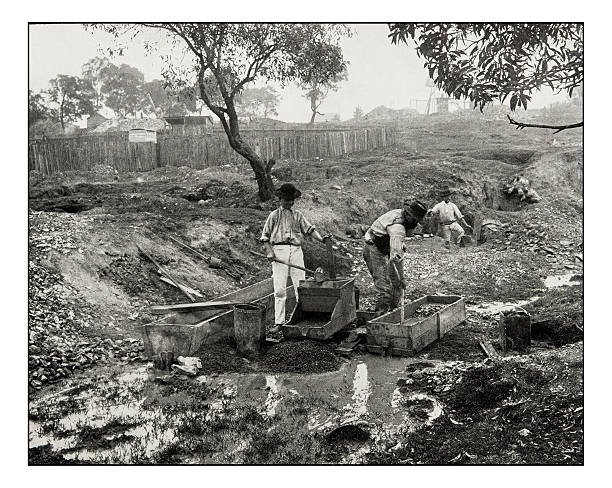
South Africa has played a central role in the global gold industry for over a century. Known as the birthplace of deep-level gold mining, the country was once the world’s largest gold producer .
In this article, we’ll explore what gold mining in South Africa involves, its historical significance, current status, and its impact on the economy and environment.
1. Historical Significance of South African Gold Mining
Gold was discovered in the Witwatersrand Basin in 1886, triggering the Johannesburg Gold Rush and transforming the region into an industrial hub. This discovery laid the foundation for modern South Africa and fueled economic growth for decades.
At its peak in the 1970s, South Africa produced nearly 70% of the world’s gold .

2. Major Gold Fields and Mines
The Witwatersrand Supergroup remains the most important gold-bearing geological formation in the country. Notable mines include:
- Mponeng Gold Mine – One of the deepest mines in the world (over 4 km underground).
- TauTona Mine – Formerly the world’s deepest.
- Driefontein Operations
- Savuka Mine
These mines are operated by companies like AngloGold Ashanti , Sibanye-Stillwater , and others.
3. How Gold Mining Works in South Africa
Unlike surface mining seen in other countries, South African gold mining is largely deep-level and hard-rock mining :
- Ore extraction from deep underground using vertical shafts.
- High temperatures and pressure make working conditions challenging.
- Advanced ventilation and cooling systems are required.
- Gold is recovered through complex processing involving crushing, milling, and chemical extraction.
This method is capital-intensive and labor-heavy.
4. Economic Impact of Gold Mining
Gold mining has historically been a cornerstone of South Africa’s economy:
- Created millions of jobs
- Built cities like Johannesburg
- Funded infrastructure development
- Contributed significantly to national GDP (though less so today)
Despite declining production, it still supports thousands of direct and indirect jobs.
5. Challenges Facing the Industry
Today, the sector faces several challenges:
- Depleting reserves and aging mines
- Rising operational costs and energy shortages
- Labor disputes and strikes
- Environmental concerns (e.g., acid mine drainage)
- Regulatory uncertainty and policy changes
These issues have led to reduced output and increased reliance on safer, more stable jurisdictions abroad.
FAQs
Q: Why is South Africa famous for gold mining?
A: Because of the massive Witwatersrand gold fields , which made South Africa the world’s top gold producer for much of the 20th century.
Q: Is gold still mined in South Africa today?
A: Yes, though production has declined. Several large-scale operations remain active, especially in the Free State and Gauteng provinces .
Q: What is acid mine drainage?
A: A major environmental issue caused by water reacting with sulfide minerals in exposed rock from mining—leading to toxic runoff that contaminates water sources.

