Gold mining is the process of extracting gold from the earth. It can range from small-scale artisanal operations to large multinational corporations with multi-billion-dollar budgets.
The goal is always the same: to find and recover gold-rich ore , then process it to extract pure gold bullion or refined metal.
🌍 Where Is Gold Found?
Gold is found in various geological environments, typically in two main types of deposits:
1. Placer Deposits
- Formed by erosion of gold-bearing rock, carried by water into rivers and streams.
- Found as loose particles or nuggets in sand and gravel.
- Often mined using panning, sluicing, or dredging .
2. Lode (Hard Rock) Deposits
- Gold embedded in solid rock, often quartz veins or mineralized zones.
- Requires drilling, blasting, and crushing to extract.
- Most common in major mining operations.
🔍 How Does Gold Mining Work? – Step-by-Step Process
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how gold mining works:
1: Exploration
- Geologists conduct surveys and use tools like geophysical mapping , soil sampling , and drilling to locate gold-rich areas.
- Cost: Can run into millions of dollars per project.
2: Mine Development
- Once a viable deposit is found, companies build access roads, processing plants, and other infrastructure.
- Includes obtaining permits and environmental assessments.
3: Extraction
- Gold is removed from the ground using various techniques:
- Open-pit mining (surface)
- Underground mining (deep deposits)
- Dredging (placer deposits)
4: Ore Processing
- Crushed ore is processed using methods such as:
- Gravity separation
- Flotation
- Cyanidation
- Heap leaching
5: Refining
- Extracted gold is purified using smelting or chemical processes to produce gold bars or doré bullion .
🧊 Types of Gold Mining Methods
There are several ways to extract gold, each suited to specific conditions and deposit types.
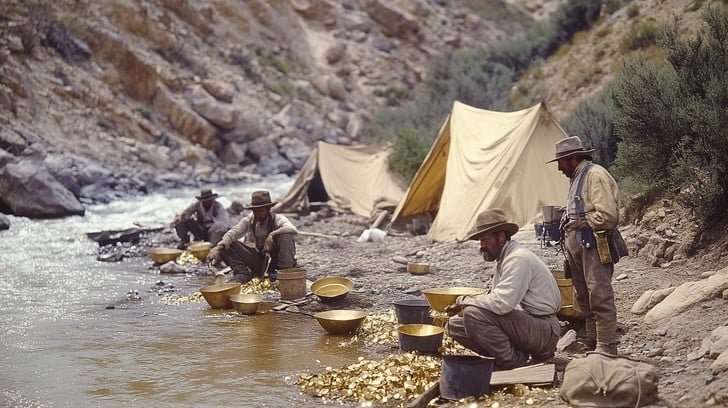
1. Placer Mining
Used for surface or streambed gold.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Panning | Manual method using a pan to separate gold from sediment |
| Sluicing | Water flows over riffled trays to trap heavier gold particles |
| Dredging | Suction dredges vacuum up riverbed material for processing |

2. Open-Pit Mining
Large-scale surface mining used when gold deposits are near the surface.
✅ Pros:
- High volume of ore extracted
- Lower operational costs than underground mining
❌ Cons:
- Major land disruption
- Dust and noise pollution

3. Underground Mining
Used when gold is deep below the surface.
Common methods include:
- Cut-and-fill
- Room-and-pillar
- Block caving
✅ Pros:
- Less surface disruption
- Access to deeper, higher-grade deposits
❌ Cons:
- More expensive
- Higher safety risks
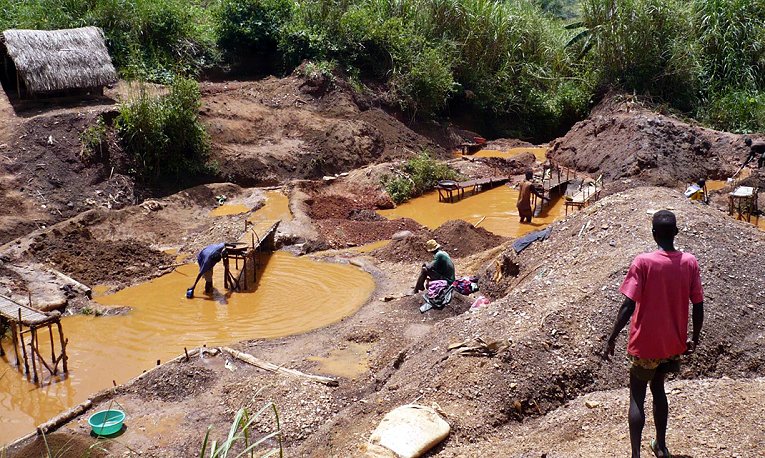

4. Heap Leaching
A low-cost method used for low-grade ores.
Process:
- Crushed ore is piled and sprayed with a cyanide solution
- The solution dissolves the gold
- Collected gold-laden solution is processed to recover the metal

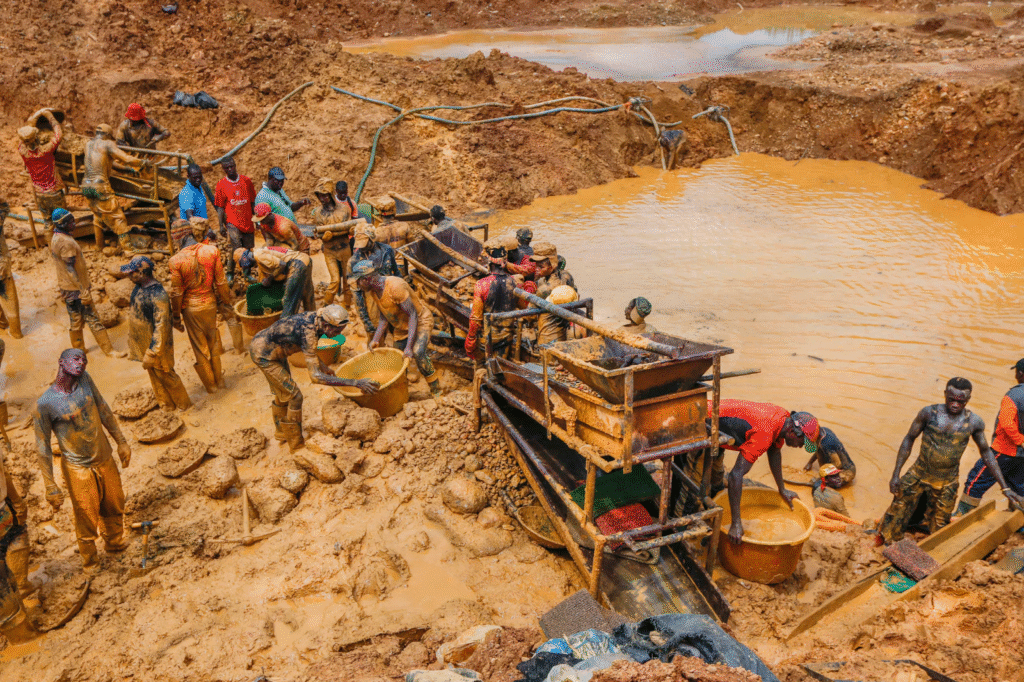
🧪 Gold Recovery Techniques
Once gold is extracted from the ore, it must be separated and purified.
Common recovery methods:
- Gravity Concentration : Uses differences in density to separate gold from waste rock.
- Flotation : Bubbles help separate gold particles from ore.
- Cyanidation : Uses cyanide to dissolve gold from crushed ore.
- Smelting : Melts gold to remove impurities and create ingots or bars.

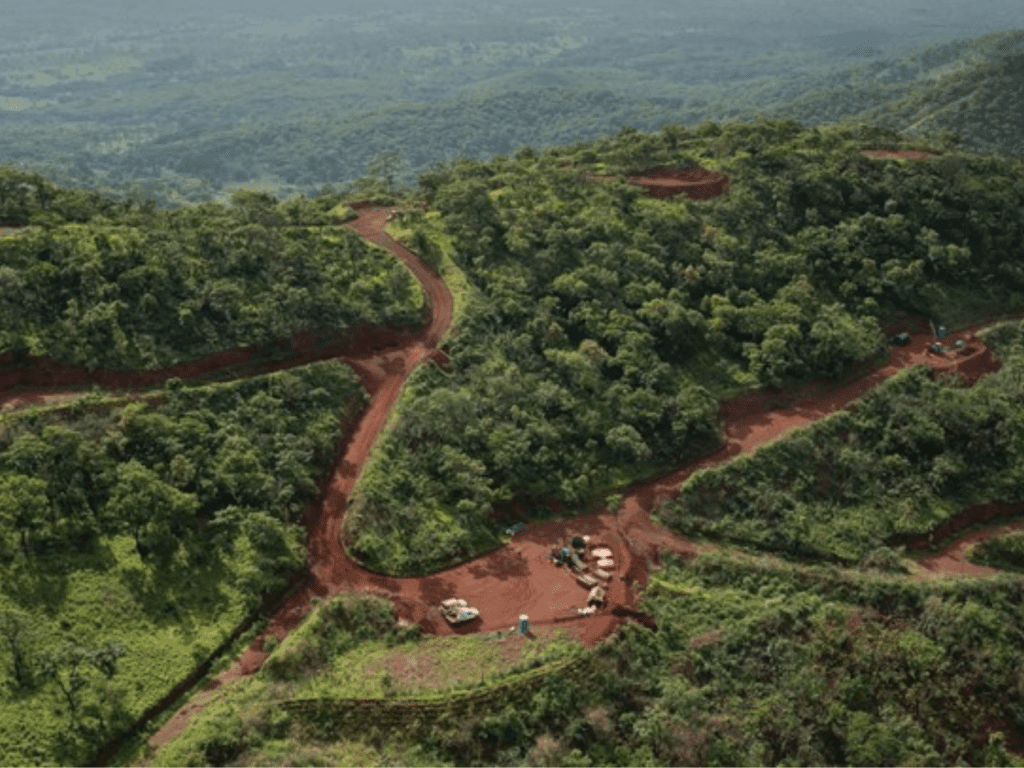
🌱 Environmental Impact of Gold Mining
While gold mining brings economic benefits, it also has significant environmental consequences:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Deforestation | Clearing land for mines destroys ecosystems |
| Water Pollution | Cyanide and mercury can contaminate waterways |
| Soil Erosion | Mining disturbs soil structure and increases runoff |
| Air Pollution | Dust and emissions from equipment and processing |
| Tailings Management | Improper disposal of mining waste can cause catastrophic failures |

🤖 Modern Technology in Gold Mining
Technology is revolutionizing how gold is mined:
- Autonomous haul trucks and drills increase efficiency and reduce labor risk.
- AI and machine learning help identify new gold-rich zones.
- Drones and satellite imaging improve surveying and monitoring.
- Sustainable practices like bio-leaching and closed-loop water systems reduce environmental damage.

💰 Economic and Global Significance
Gold remains one of the most valuable commodities in the world:
- Central banks continue to buy gold for reserves.
- Jewelry demand remains strong in Asia and the Middle East.
- Gold is used in electronics, dentistry, and aerospace.
Countries like China, Russia, Australia, Canada, and Ghana lead global production.
Final Thoughts
Gold mining is a blend of science, engineering, and resourcefulness . Whether it’s a lone prospector panning for flakes in a creek or a multinational company running a massive open-pit operation, the goal is the same: to bring gold from the earth to your hand.
Understanding how gold mining works helps us appreciate both its value and its impact — not just economically, but environmentally and socially too.
As technology improves and sustainability becomes more important, the future of gold mining looks increasingly innovative — and hopefully, more responsible.
FAQs
Q1: How does gold mining work?
Gold mining involves locating, extracting, and processing gold from the earth using methods like placer mining, open-pit mining, or underground mining , followed by ore processing and refining .
Q2: What are the main methods of gold mining?
The main methods are:
- Placer mining (riverbeds and streambeds)
- Open-pit mining (surface extraction)
- Underground mining (deep deposits)
- Heap leaching (chemical extraction of low-grade ore)
Q3: Is gold mining dangerous?
Yes, especially underground mining, which carries risks like cave-ins, gas exposure, and equipment failure. However, modern safety standards have significantly reduced workplace hazards.
Q4: How much does it cost to mine gold?
Costs vary widely based on location, method, and ore grade. On average, it costs $300–$1,200 per ounce to mine gold, depending on the region and operation scale.
